
Before discussing how to run payroll for an S Corp owner, let’s briefly recap what an S Corp is. An S corporation is a business that has the benefits of a typical corporation business structure—without double taxation. S Corp Payroll Shareholders pay income taxes on their earnings, but the business itself does not pay income tax. The 60/40 rule is a simple approach that helps S corporation owners determine a reasonable salary for themselves.
How are LLCs taxed? LLC tax benefits and tips to reduce taxes
Aside from its tax status, an S corp is similar to any other corporation, or C corporation as they’re officially known. An S corp is a for-profit company, incorporated under and governed by the same state corporation laws. It offers similar liability protection, ownership, and management advantages as a C corp. Navigating the full range of deductions, credits, exemptions, and options is no easy feat, and without professional help, the likelihood that money will be left on table is much higher, as is the risk of being audited. Hiring a full-time accountant for the business is of course an option too—and their salary is tax-deductible.
Payroll services for S corporations
- Instead, you use a payroll service to pay yourself employee wages and to take care of any required taxes and regulations.
- Get up and running with free payroll setup, and enjoy free expert support.
- The definition of an employee for FICA (Federal Insurance Contributions Act), FUTA (Federal Unemployment Tax Act) and federal income tax withholding under the Internal Revenue Code includes corporate officers.
- Keep in mind that if you disburse money to yourself for shareholder distributions at other times throughout the year, you will categorize those payments as shareholder distributions rather than wages.
- And if you operate in a state like this, you may only need to prepare and file the federal 941 tax returns over the course of a year.
In return for this tax benefit, S corps face certain IRS-mandated restrictions. S corps combine the benefits of corporations with the tax advantages of partnerships. They offer the limited liability protection of the corporate structure—meaning that an owner’s personal assets can’t be accessed by business creditors or legal claims against the company. But like partnerships, they don’t pay corporate taxes on any earnings and income that they generate.
IRS e-file rejection grace period of timely-filed returns and extensions
The IRS determines the amount you owe based on your wages, which excludes other sources of S corp income, like distributions or dividends. ADP understands that payroll can be challenging, even for S corporations with just a few employees or a single individual wearing many hats. We offer payroll services that are designed to help small business owners minimize administrative burdens, so they can focus more of their time on what made them want to be an entrepreneur in the first place. Courts have found shareholder-employees are subject to employment taxes even when shareholders take distributions, dividends or other forms of compensation instead of wages. The definition of an employee for FICA (Federal Insurance Contributions Act), FUTA (Federal Unemployment Tax Act) and federal income tax withholding under the Internal Revenue Code includes corporate officers.
U.S. Income Tax Return for an S Corporation
The fact that an officer is also a shareholder does not change this requirement. Courts have consistently held S corporation officers/shareholders who provide more than minor services to their corporation and receive, or are entitled to receive, compensation are subject to federal employment taxes. The Five Minute Payroll monograph explains how to do simple cookie-cutter payroll for most one-employee S Corporations using base salary amounts of $10,000 a quarter or $16,000 a quarter. Furthermore, the e-book provides some common-sensed tips you can use to set a reasonable salary for your S corporation and to minimize your state payroll taxes burden, too. Some of the quarterly state returns amount to simple worksheets that, for example, levy a 3% tax on wages for state unemployment insurance premiums.

You can determine precisely how much federal income tax you should pay over the year by downloading the 1040-ES estimated tax payments form from the website and completing the tax liability worksheet included with that form. New business owners must face an oft-confusing set of choices around the labels S-corps, C-corps and LLCs. The most important https://www.bookstime.com/ thing to know about S-corps when deciding between establishing your business and electing among various structures and tax statuses is that an S-corp is not a business structure. While corporations and LLCs are both types of legal entities, an S-corp is a tax status (or tax designation) with certain added advantages and restrictions.
- If you sign up for a membership with Collective, you get a membership at leading payroll provider Gusto, one of Collective’s partners.
- The IRS treats stock as being in one class if all shares have equal rights to distribution and liquidation proceeds.
- Pay frequency laws tend to require more frequent pay periods for employees.
- Shareholders can be individuals, certain trusts and estates, but cannot be nonresident aliens, corporations or partnerships.
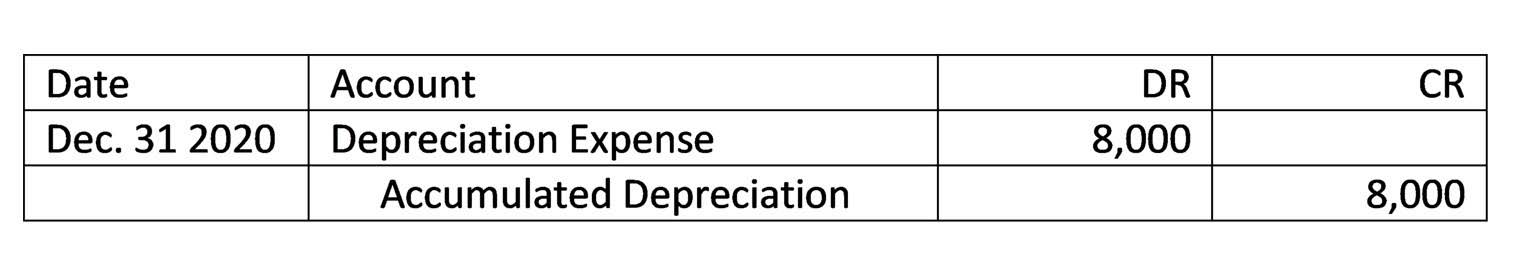
As noted earlier, if you make additional disbursements to the shareholder (and hopefully you will be doing this), you categorize these amounts not as wages but as shareholder distributions. You also need to check the right “Report For This Quarter” box in the upper right corner of page 1 (check January, February, March for the first quarter, for example). Note also that your state and whether or not you send in a payment determines which address to send the form to. But all the other information shown on the 941 in boxes 1 through 15 and on the 941-V would match what I’ve plugged in here.

Business Line of Credit: Compare the Best Options
Any violation of Chapter 100 is subject to the excise tax under IRC § 4980D ($100 per affected person per day), unless the IRS waives all or part of the excise tax upon a showing of reasonable cause and no willful neglect. All full-time employees must be eligible for the QSEHRA after a waiting period of no more than 90 days of service. There are certain permitted exclusions, such as for employees under age 25 and union employees. A QSEHRA may be funded only by the employer, not by employee salary reductions.